Function calculator
All functions are created in the Function calculator. Nodes, numbers, mathematical operators, and time functions can be used to build functions.
If nodes are used in a function, the function must contain the following information:
-
Node(s) - chosen by the user
-
Node type - set automatically by the system or chosen by the user
-
Time period - set automatically to BOP,EOP (BOY,EOY when using YTD) or specified by the user, see Information period and Time functions
-
Organization - set automatically by the system or manually by the user
The following is an interactive screen. Click on the different parts of the calculator for more information:
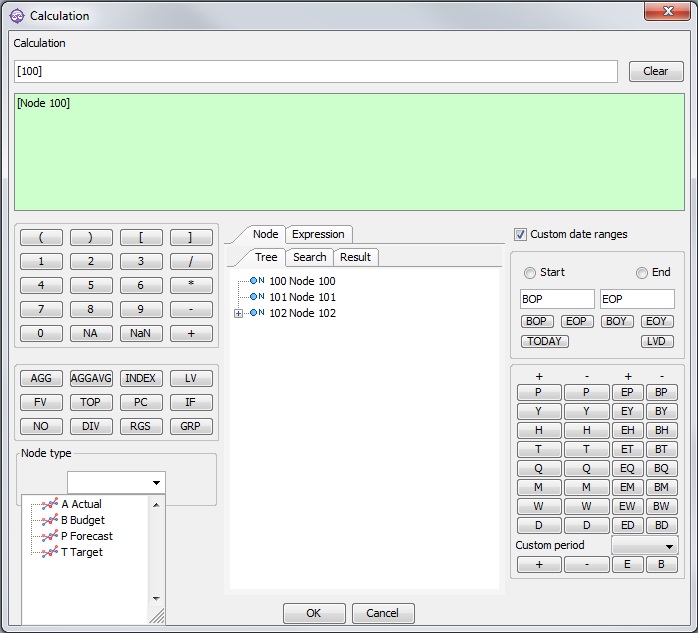
How it works
To create a valid function, you must first decide which function, organization(s), node(s), and node type to use. You must also decide whether you want to use the default time period (BOP,EOP) or create a different time period.
'BOP,EOP' is implicit in each node if nothing else is specified ([node, bop,eop]). This means that it is always the current period and the Information period that control which data are retrieved. If the Information period is yearly, it is always the current year's data that are retrieved, if it is monthly, the current month's data, etc.
If you want to use a different Time period, create the Start and End functions before you define the function itself. Mark the Custom date ranges checkbox. Then mark Start and create the start function using the buttons provided. Then mark End and create the end function in the same way. For more information see the Time functions section.
 Instead of Start and End functions, fixed dates in the format YYYY-MM-DD may be used, e.g. AGG('[100,2013-01-01,2013-12-31]',100), NOD(2014-01-01,2015-01-01), etc.
Instead of Start and End functions, fixed dates in the format YYYY-MM-DD may be used, e.g. AGG('[100,2013-01-01,2013-12-31]',100), NOD(2014-01-01,2015-01-01), etc.
 When you choose to show Year to date figures, BOP and EOP are replaced with BOY and EOY. To avoid this, replace BOP with EOP+BM in the calculator: [node,eop+bm,eop]
When you choose to show Year to date figures, BOP and EOP are replaced with BOY and EOY. To avoid this, replace BOP with EOP+BM in the calculator: [node,eop+bm,eop]
When you have defined the time period, choose the function button on the left that corresponds to the function you want to create.
For details about creating a specific function, see the corresponding section on the function type. See also Function syntax.
Using Expressions
Function expressions and Query expressions can be found in a separate tab in the Function calculator. To use an expression in a calculation, click the Expressions tab and choose the desired expression. It will be added in the Calculation field as:
{expression ID}
You can also enter an expression ID directly into a Function using the format {expression ID}.
 Nodes and Expressions can be created directly in the corresponding tab in the Function Calculator. Right click in the desired tab and choose Add -> Node or Function expression from the menu. Then right click on the node or expression and choose Edit from the menu to configure it. See Node management or Expressions for more information.
Nodes and Expressions can be created directly in the corresponding tab in the Function Calculator. Right click in the desired tab and choose Add -> Node or Function expression from the menu. Then right click on the node or expression and choose Edit from the menu to configure it. See Node management or Expressions for more information.
Using Tags
It is also possible to refer to Reporter tags as properties in functions. Enter tags directly in the Function field or click the Tags tab in the Function calculator and select.
Tags should not contain white spaces, especially between $ and {.
E.g. $ { this.object.id } could be misinterpreted. The correct syntax is ${this.object.id}.
Some examples of use
-
${this.object.progress} - will give the progress value of the current object
-
${this.object.customNumberProperty} - will give the value of a custom number property of the KPI
-
AGG('[100]',${this.organisation.id}) - will be identical to AGG('[100],this)
-
AGG('[100]',${this.object.orgReference.id}) - uses a custom reference property on the object, to refer to the organization to be used in the AGG function
-
AGG('[100]',*this) as '${this.object.name}' - gives the AGG function the same name as the KPI the function is on; will only be displayed when Include top row is marked
-
IF ${this.object.showTabs} THEN 1 ELSE 0 - will give the value 1 if the Show Tabs property on the object is checked
-
[100,2014-05-01,2014-05-01+em] - will calculate the value for May 2014. Adjusting functions may also be used.
-
[100,${t.123.startDate},${t.123.startDate}+em] - will calculate the value based on the Start and End date; date modifiers may also be used
-
[${this.object.customProperty}] - will calculate that the node has the same ID as the chosen property in the customProperty for the current web parent (of the function)
-
${this.object.id} - will give the ID of the current object
 In this case the ID is text and not a number. The calculator can only return numbers at the current time, so using ${this.object.id} only, will not produce a valid function. You can however use the function [${this.object.id}] to refer to a node with the same ID as the current object.
In this case the ID is text and not a number. The calculator can only return numbers at the current time, so using ${this.object.id} only, will not produce a valid function. You can however use the function [${this.object.id}] to refer to a node with the same ID as the current object.
This is also the case with dates. Since dates are not numbers, they will not produce valid functions, and the result will usually be NA.
 ${this.object} is the nearest web parent of the function ("current object"), so a function on a KPI will refer to the KPI if ${this.object.xxx} is used.
${this.object} is the nearest web parent of the function ("current object"), so a function on a KPI will refer to the KPI if ${this.object.xxx} is used.
 At the current time, tags can only be validated in the Preview panel. Syntax errors are reported correctly in the calculator, but the description zone in the calculator stays green if the function contains invalid references. The Preview panel will display a text area with any errors if the function is incorrect when previewed.
At the current time, tags can only be validated in the Preview panel. Syntax errors are reported correctly in the calculator, but the description zone in the calculator stays green if the function contains invalid references. The Preview panel will display a text area with any errors if the function is incorrect when previewed.
 Calculations change because referring objects change, e.g. historical properties, so a standard chart can show progress over time.
Calculations change because referring objects change, e.g. historical properties, so a standard chart can show progress over time.
Other examples
-
AGG('[100]',${this.object.ref}) - uses the contents of the non-rich text custom property "ref" on this.object as the organization reference in the AGG function:
-
if ${this.object.ref}) contains 100, the function resolves to
-
AGG('[100]',100)
-
-
if ${this.object.ref}) contains 100, 200, the function resolves to
-
AGG('[100]',100,200)
-
AGG('[100]',${this.object.orgRef}) - uses the content of the custom reference property ${this.object.orgRef} as the organization reference in the AGG function:
-
where orgRef is a custom single reference property with a reference to an organization, it will resolve to that organization
-
where orgRef is a custom multi reference property with a reference to multiple organizations, it will resolve to those organizations
-
Warning
${this.object.relValue} will give the relative value (relValue) of the current object. This can introduce an infinite loop as the function might be used to calculate the relValue of the KPI.